[Major points]
- Hypoglycemia is defined as a blood glucose level lower than 70 mg/dL.
- Common symptoms include hunger, trembling, and cold sweating; in severe cases, it could lead to unconsciousness.
- When experiencing hypoglycemia, follow the 15 rule for immediate management; if condition does not get better, seek medical attention immediately.
- It is important to understand the causes of hypoglycemia to prevent recurrence in the future.
What is hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia is defined as a blood glucose level lower than 70 mg/dl. Untreated hypoglycemia for an extended period, could lead to brain damage, loss of consciousness, and even life-threatening events. It is an acute complication of diabetes and requires immediate management. Especially for long-term diabetic patients, the response reaction of hypoglycemia is destroyed, and it is easy to cause severe hypoglycemia symptoms.
What are the causes of hypoglycemia?
There are many reasons for hypoglycemia. The patient may have diabetes or it may not be related to diabetes. The common reasons are as follow:
- Diet: Reduced food intake, taking oral hypoglycemic agent or insulin without eating, skipping meals, drinking alcohol on an empty stomach.
- Medications: Excessive dosage of oral hypoglycemic agent or insulin injections, self-adjustment of medication dosage and timing.
- Exercise: Increased physical activity, exercising on an empty stomach.
- Non-diabetes related factors: Thyroid dysfunction, insulinoma, insulin autoimmune syndrome (a rare autoimmune disease that can cause hypoglycemia), etc.
- High risk factors: History of severe hypoglycemia, long-term diabetes history, impaired liver or kidney function, depression, or mental stress, etc.
What are the common symptoms?
Symptoms of hypoglycemia will vary from person to person, and may have different symptoms each time.
- Autonomic symptoms: These are mild symptoms of hypoglycemia and may include hunger, trembling, sweating, rapid heartbeat, tingling sensations in the limbs, nervousness, and anxiety.
- Neuroglycopenic symptoms: These include slurred speech, inability to concentrate, weakness in the limbs, dizziness, blurred vision, drowsiness, confusion, and unusual behavior. In severe cases, it may lead to convulsions and unconsciousness.
- Unaware hypoglycemia: Some long-term diabetes patients, elderly diabetics, or those who tightly control their blood sugar may experience hypoglycemia with subtle or no autonomic symptoms, directly showing neuroglycopenic symptoms.
It dont't mean you must have hypoglycemia with above symptoms, if you have the above symptoms, please seek medical assistance at the Endocrinology & Metabolism clinic.
What are the common treatment methods?
- The 15 rule for hypoglycemia: If you have symptoms of hypoglycemia with clear conscious, measure blood glucose immediately (if glucose meter is unavailable, then intake food immediately), and ingest 15 grams of sugary food (three sugar cubes, 1 level tablespoon of granulated sugar, 1 bottle of lactobacillus drink, approximately 150mL of sugary drink, or 120mL of fruit juice). After 15 minutes, check blood glucose again. If the blood glucose remains below 70 mg/dl, repeat the treatment. If blood glucose is still below 70 mg/dl after repeat treatment 2 times or consciousness is impaired, seek medical assistance immediately (figure 1).
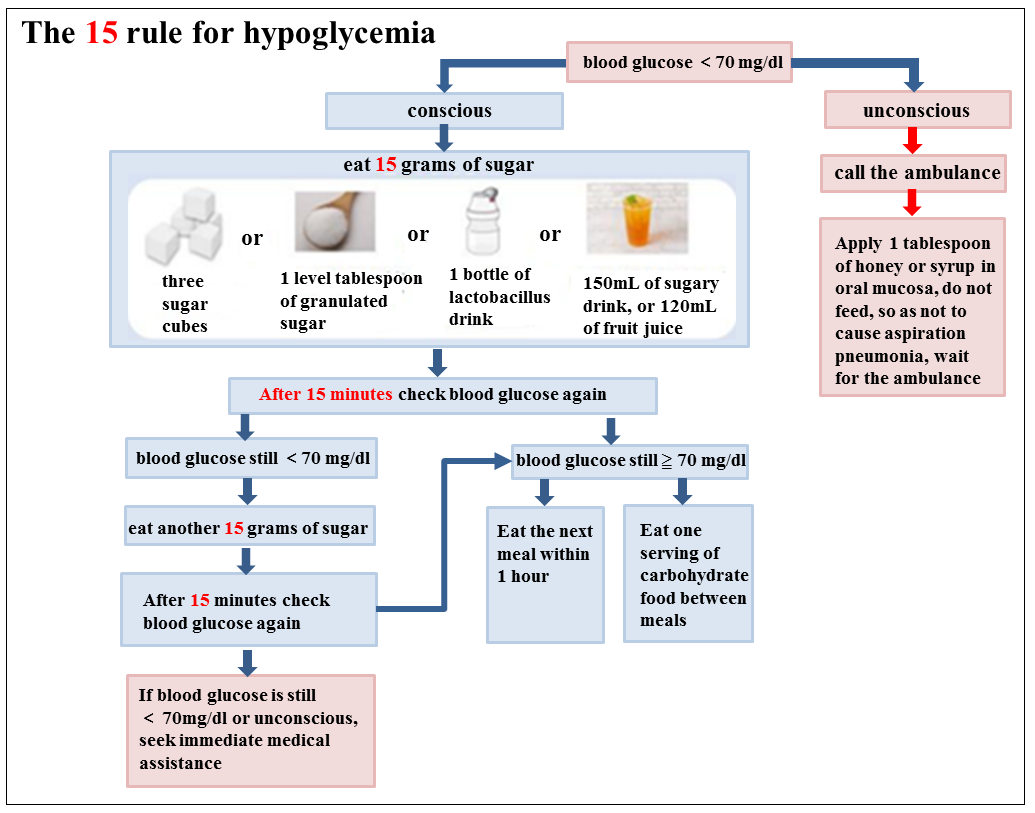
figure 1 The 15 rule for hypoglycemia - When hypoglycemia symptoms improves, supplement one serving of carbohydrate food, such as one slice of thin toast or three slices of soda crackers if there is still more than 1 hour before next meal. It would help preserve energy, stablize blood glucose level , and prevent hypoglycemia recurrent(figure 1).
- When taking Acarbose (Glucobay®), it is necessary to use glucose tablets or milk as a treatment when experiencing hypoglycemia.
- Foods not recommended during hypoglycemia:
- Sugar substitutes such as saccharin, aspartame, etc., which do not raise blood sugar levels.
- High-fat foods such as chocolate, ice cream, etc., because fats can slow down the absorption of glucose, leading to a slower increase in blood sugar levels.
- When a patient is unable to swallow or is unconscious, they should be immediately taken to the hospital. If you are a family member, here is how you can assist:
- Do not inject insulin.
- Help the patient's head turn to one side in order to keep the airway open, not forcibly feed. Give the patient sugar syrup or honey 1 tablespoon directly on the oral mucosa with plastic dropper and massage till it is absorbed. The patient should be taken to hospital immediately.
Principles of care:
- Follow the prescription of oral hypoglycemic agent and insulin dosage by the doctor.
- Regularly self-monitoring blood glucose levels. If the bedtime blood glucose is below 110 mg/dl, it is necessary to supplement with carbohydrate food such as three pieces of soda crackers and 240 mL of milk to prevent nocturnal hypoglycemia.
- Eat meals regularly at fixed times; avoid exercising on an empty stomach, and if engaging in intense physical activity, consume extra carbohydrate food; avoid drinking alcohol on an empty stomach.
- When getting sick and diarrhea or reduced appetite, you can substitute regular meals with sports drinks, sugary drinks, milk, and other liquid foods and closely monitoring blood glucose levels.
- When going out, carry sugar tablets, and bring the diabetes mellitus identification card at all times.
- Find out the causes of hypoglycemia and prevent it happen again. Encourage family and friends learn to recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia so that they can provide immediate assistance in case of an emergency.
References
- American Diabetes Association (2022). Standards of care in diabetes-2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical Diabetes, 41(1), 4-31. https://doi.org/10.2337/cd23-as01
- Lebras, M., & Laubscher, T. (2021). Hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes. Canadian Family Physician, 67, 35-38. https://doi.org/10.46747/cfp.670135
- Lo, F. S. (2020). Frequency, causes, risk factors and management of hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Formosan Journal of Medicine, 24(3), 280-288. http://doi.org/10.6320/FJM.202005_24(3).0006
- Pei, D. (2020). Causes, risk factors and management of hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes. Formosan Journal of Medicine, 24(3), 289-293. http://doi.org/10.6320/FJM.202005_24(3).0007
- Taiwanese Association of Diabetes Educators (2022). 2022 Diabetes education core textbook. Taiwanese Association of Diabetes Educators.
- The Diabetes Association of the Republic of China (2022). Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes care 2022. The Diabetes Association of the Republic of China.
- Yang, W. S. (2020). Normal glucose metabolism and hypoglycemia reaction. Formosan Journal of Medicine, 24(3), 272-274. http://doi.org/10.6320/FJM.202005_24(3).0004
Quiz
Please answer the following questions:
Nursing Instruction Satisfaction
Please log in to rate
- Location
-
- Category
- Disease