【Major Points】
- Common symptoms include eating more, drinking more, and urination more, or weight loss.
- Treatment methods can be categorized into three aspects: diet, exercise, or medication.
- It is recommended to maintain fasting blood sugar levels between 80-130 mg/dL (80 to 130 milligrams of glucose per 100 milliliters of blood).
- It is recommended to keep HbA1c levels below 7%.
What is diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes is caused by defects in insulin secretion or poor functioning of the
pancreas, resulting in glucose in the blood not being converted into calories for the body to use, which increases the blood sugar level. When blood glucose rises to the limitation that can be recovered by the kidneys, glucose in the urine will appear, hence the name diabetes.
There are four types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus:
- Pancreatic beta cell, which produces insulin in the pancreas,are destructed by auto-immune system or by unknown etiologies. As a result, pancreas fails to secrete insulin.
- Lifelong insulin injections are required to control blood sugar.
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus:
- Insufficient insulin secretion due to diet, obesity, low activity and genetics; or the body's cells resistant to insulin and insulin does not work, resulting in increased blood sugar.
- The most common diabetes type.
- Gestational diabetes mellitus: It occurs as the result of hormonal changes during pregnancy or insulin-blocking hormones produced by the placenta. This causes blood sugar to rise.
- Others: Diabetes caused by inflammation of the pancreas, removal of the pancreas, genetic abnormalities, long-term use of steroid drugs, etc..
What are the symptoms of diabetes mellitus ?
- Symptoms of eating more, drinking more, and urination more.
- Weight loss.
- Weakness, fatigue.
- Blurred vision.
- Slow-healing wounds.
- Easy urinary tract inflammation.
Those who have the above symptoms are not necessarily diabetes. If you have the above symptoms, please go to the endocrinology & metabolism clinic for consultation.
How is diabetes mellitus treated?
The treatment of diabetes can be divided into three aspects: diet, exercise and drugs. Generally, diet and exercise will be adjusted first. When blood sugar cannot be well controlled under diet and exercise therapy, drug is required, such as oral hypoglycemic drugs or insulin to control blood sugar.
How can I take care of myself if I have diabetes mellitus?
- Monitor blood sugar:
- Follow the prescription that doctor prescribed, as well as taking oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin injection regularly. Do not increase, decrease, or quit the medicine without permission.
- Daily self-monitoring and recording of blood sugar for reference in treatment.
- Understand the symptoms and treatment of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and increase self-care ability. (More information: Care of Patient with Hypoglycemia, Care of Patient with Hyperglycemia)
- Maintain a good lifestyle:
- Diet regularly and quantitatively, and control the amount of carbohydrate food in each meal.
- Regular and appropriate exercise to maintain ideal body weight.
- Daily oral hygiene, body cleaning and foot care.
- Self-adjustment of stress and maintenance of mental health.
- Quit smoking and alcohol drinking.
- Regularly return to the outpatient clinic for follow-up, and follow the doctor's arrangement to track HbA1c (glycosylated hemoglobin), renal function and eye examination.
How do I know if my diabetes is well controlled?
Glycemic targets for adult with diabetes:
- Fasting blood sugar is 80-130mg/dL (80 to 130 milligrams of glucose per 100 milliliters of blood).
- Blood sugar below 180 mg/dlL (180 milligrams of glucose per 100 milliliters of blood) two hours after meals.
- The HbA1c (glycosylated hemoglobin) should be less than 7% in blood sampling every 2-3 months (Figure 1), which can prevent the occurrence of chronic complications of diabetes.
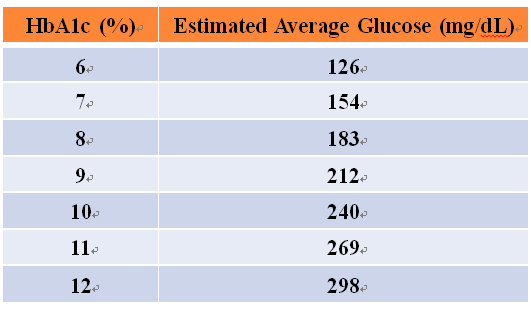
Figure 1 The average blood sugar value represented by HbA1C
Reference
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee (2024). Comprehensive medical evaluation and assessment of comorbidities: Standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care, 47(Suppl 1), S52-76. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc24-S004
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee (2024). Diagnosis and classification of diabetes: Standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care, 47(Suppl 1), S20-S42. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc24-S002
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee (2024). Glycemic goals and hypoglycemia: Standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care, 47(Suppl 1), S111-S125. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc24-S006
- The Diabetes Association of the Republic of China (Taiwan) (2022). Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes care 2022. The Diabetes Association of the Republic of China(Taiwan).
Quiz
Please answer the following questions:
Nursing Instruction Satisfaction
Please log in to rate
- Location
-
- Category
- Disease