【Major Points】
- What is abdominal pain? What are the symptoms?
- How can I take care of myself when I have abdominal pain?
- What are associated symptoms of abdominal pain that you should seek immediate medical attention?
What is abdominal pain?
Abdominal pain is a discomfort in your belly region, which contains many organs. Therefore, many different conditions may cause abdominal pain. The following causes of pain are shown by simply dividing the abdomen into four quadrants (Picture 1):
- Left upper quadrant (LUQ): indicates possible illness related to the left side of the stomach, or spleen, etc.
- Right upper quadrant (RUQ): indicates possible illness related to liver, gallbladder, or duodenum, e.g. cholecystitis, duodenitis.
- Left lower quadrant (LLQ): indicates possible illness related to sigmoid, kidney, or gynecology, e.g. diverticulitis, constipation, etc.
- Right lower quadrant (RLQ): indicates possible illness related to appendix, kidney, or gynecology, e.g. appendicitis, kidney stones, etc.
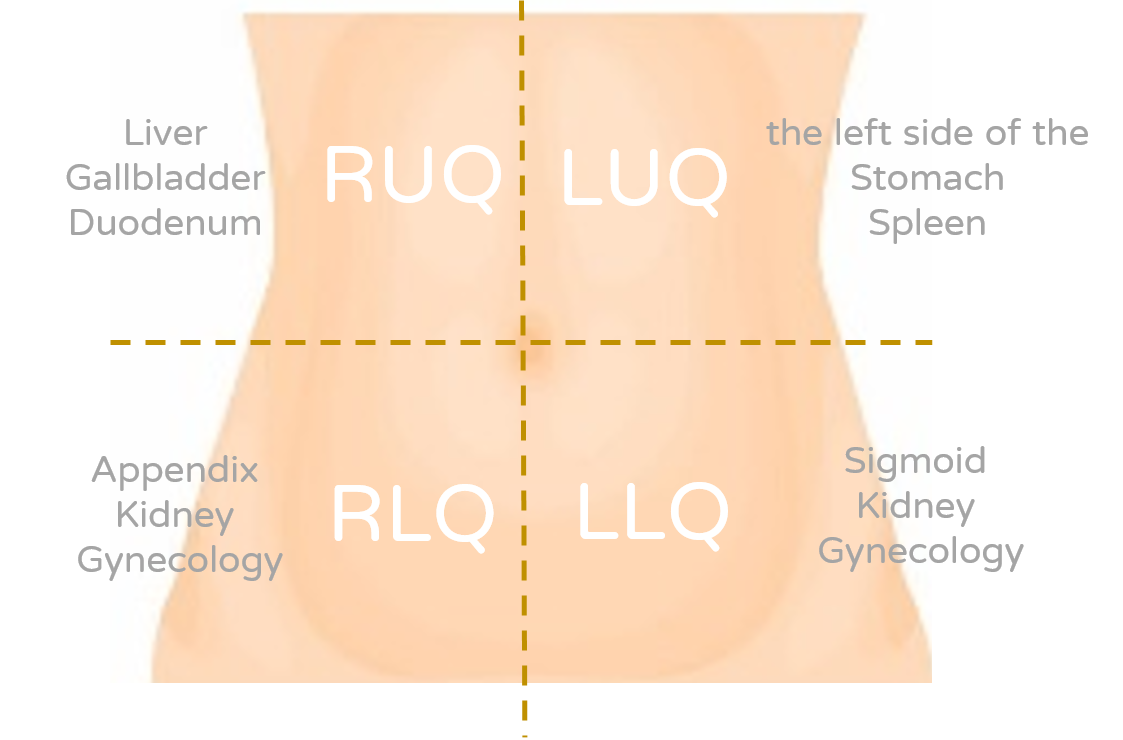
(Picture 1 Possible diseases associated with the location of abdominal pain )
What are the common symptoms of abdominal pain?
Abdominal pain does not always occur in the abdomen, but is commonly caused by a problem in the gastrointestinal tract, e.g. gastroenteritis, constipation, or flatulence, etc. Thus, physician assessment and appropriate exams are required. You should seek medical attention if you have abdominal pain. (Make an appointment: Gastroenterology)
Some serious types of abdominal pain that may require medication or immediate surgery, such as bowel obstruction, hernia, appendicitis, and intestinal perforation, etc. If it happens, you may be in a life-threatening, so you should go to the hospital as soon as possible. For instance, persistent abdominal pain accompanied by other symptoms e.g. bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, cold sweating, trouble breathing, dizziness, pale face, generalized weakness, and/or abdominal pain that occurred after injuries, you should visit the emergency room immediately.
Abdominal pain does not always occur in the abdomen, but is commonly caused by a problem in the gastrointestinal tract, e.g. gastroenteritis, constipation, or flatulence, etc. Thus, physician assessment and appropriate exams are required. You should seek medical attention if you have abdominal pain. (Make an appointment: Gastroenterology)
Some serious types of abdominal pain that may require medication or immediate surgery, such as bowel obstruction, hernia, appendicitis, and intestinal perforation, etc. If it happens, you may be in a life-threatening, so you should go to the hospital as soon as possible. For instance, persistent abdominal pain accompanied by other symptoms e.g. bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, cold sweating, trouble breathing, dizziness, pale face, generalized weakness, and/or abdominal pain that occurred after injuries, you should visit the emergency room immediately.
Care Instructions:
- The following steps may help prevent abdominal pain:
- Eat small frequent meals, chew carefully and swallow slowly, avoid greasy foods.
- Drink plenty of water (without pre-existing medical condition), 1500-2000cc per day.
- Exercise regularly.
- Limit food items that produce gas, e.g. onions, green peppers, sweet potatoes, soft drinks, fried foods, and high-sugar desserts, etc.
- Make sure that your meals are well-balanced with higher amount of fiber (e.g. whole grains, beans, dried fruits, etc.). Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- The following steps may reduce mild abdominal pain:
- Avoid solid food within the first 4-6 hours, then start with water or clear liquid.
- If you have been vomiting:
- Stop eating, wait till the vomiting stop, and have a sip of water.
- Wait for 6 hours and consume small amount of mild food items such as rice, applesauce, or crackers.
- Avoid dairy products.
- More information: Care of Children with Gastroenteritis.
- If the pain occurs after the meal:
- When the pain is located above the abdomen, it may be gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). In this case, antacids may help, especially if you feel heartburn (a burning feeling in the chest) or indigestion (upper abdominal fullness).
- More information:Care of Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disorder
- Avoid citrus, high-fat food, deep fried food, tomato products, caffeine, alcohol, and carbonated beverages.
- Take your pain medicine as prescribed:
- Take your medicine as prescribed only, or else the pain may be masked and altered the diagnosis.
- Do not self medicate with aspirin, ibuprofen, or other anti-inflammatory medication.
- Seek medical help if the pain does not reduce.
References
- Jonathan, S.S. (2018). Urachal remnants in patients presenting to the emergency department with abdominal pain. The Journal of Emergency Medicine, 55(3), 333-338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2018.05.023
- Pemmerl, S., & Hüfner, A. (2020). Epidemiology, initial diagnosis, and therapy of unexplained abdominal pain in the emergency department. Medizinische Klinik, Intensivmedizin und Notfallmedizin, 116(7), 578-585. https://10.1007/s00063-020-00696-x
- Zao,Z., Heath,C., &Ting, Gong. T. (2019). Fever, abdominal pain, and jaundice in a pacific islander woman. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 323(3), 272-273. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.20118
Quiz
Please answer the following questions:
Nursing Instruction Satisfaction
Please log in to rate
- Location
-
- Category
- Self-care / Home Care