【Major Points】
- Do not eat any food, drink water or beverages during preoperative fasting.
- The postoperative wound should be kept clean and dry.
- Continue to perform various rehabilitation exercises after surgery.
- When getting out of bed and walking, pay attention to safety and prevent falls.
I. What is artificial knee replacement?
The diseased femoral and tibial articular surfaces are partially resected and replaced with alloy artificial knee articular surfaces.
II. Why is this surgery needed?
- Restore the original smooth and normal angle of the knee joint and relieve joint pain.
- Improve the quality of life.
III. Preparation before surgery:
- The preoperative tests includes electrocardiography, chest x-rays, and blood tests.
- The doctor will explain the process and the purpose of the operation to the patient and family. The patient will sign an operation consent form, anesthesia consent form, blood transfusion consent form, and self-pay consent form.
- In order to observe the patient’s skin color during anesthesia, prior to operation, nail polish and lipstick must be removed.
- To avoid anesthesia risk of vomiting, the patient cannot eat or drink anything for at least eight hours before surgery. After patient returns to the ward, the eating instructions must be followed.
- On the morning of surgery, the patient will change into a surgical gown and will be required to remove dentures, watches, and jewelry, etc.
IV. Post-operative care:
- The patient must keep his/her knees straight. If the leg swelling is severe, pillows can be used to elevate the calf. Do not place pillows under the knees.
- To prevent pressure injury, the patient should change position at least every two hours.
- Ambulation is suggested on the next day after surgery. When you are the first time of ambulating, your nurse will assist you and teach you how to use the crutches or walkers (More information: Use of Crutches or Walker).
- Rehabilitation:
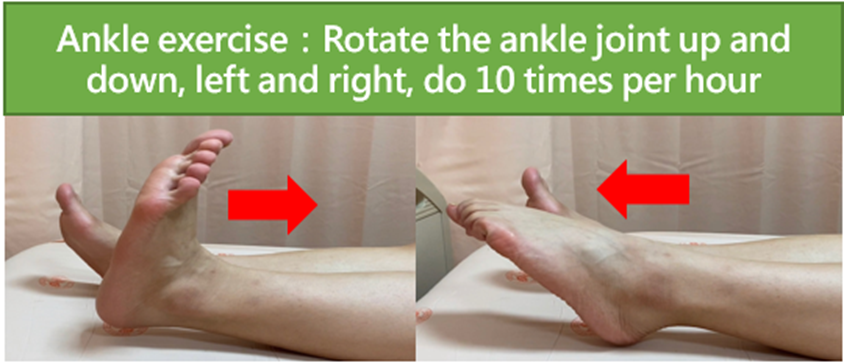
- Ankle pumping: Move your ankle all the way up and all the way down. Rotate your ankle left and right. Repeat 10 times per hour (Figure 1).
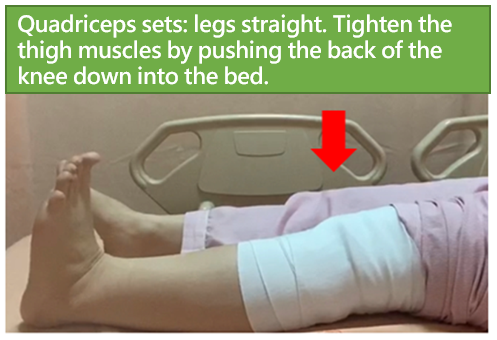
- Quadriceps sets: Lie on back with legs straight. Tighten the thigh muscles by pushing the back of the knee down into the bed. Hold the contraction for five seconds and then release. Repeat 10 times(Figure 2).
- Knee flexion and stretch exercise.
- Lie down and flex the operated leg, then slowly stretch it out as much as possible (Figure 3).

- Follow the doctor’s order to use a continuous passive motion (CPM) machine once or twice a day for about 15 minutes to help the knee flexion and stretch. Applying an ice pack and pressure on the affected leg may relieve the pain and swelling (Figure 4).

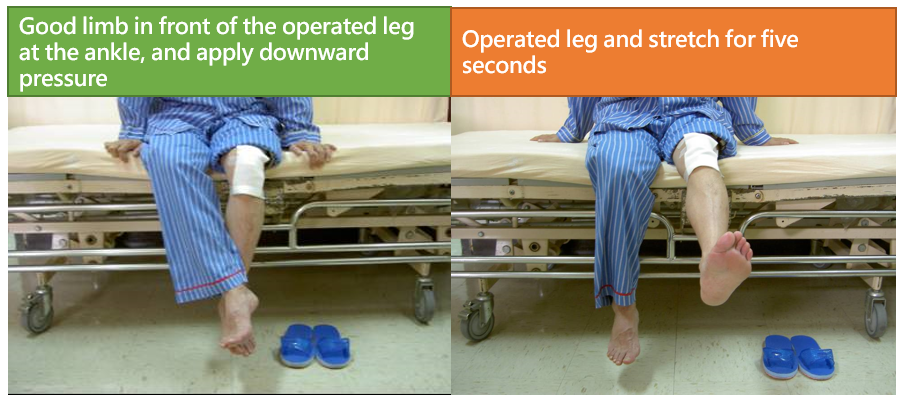
- Sitting on the edge of a bed or chair, place the good limb in front of the operated leg at the ankle, and apply downward pressure for five seconds. Next, raise the operated leg and stretch for five seconds, then slowly put it down. Repeat 10 times. 3-5 secessions per time(Figure 5).
- Lie down and flex the operated leg, then slowly stretch it out as much as possible (Figure 3).
- Ankle pumping: Move your ankle all the way up and all the way down. Rotate your ankle left and right. Repeat 10 times per hour (Figure 1).
V. Self-care at home:
- Please keep the wound clean and dry. Have your first post-operative follow up appointment, which is usually10-14 days after discharge. Before you take a shower, your doctor needs to check your wound or remove the stitches.
- After returning home, please continue to perform various rehabilitation exercises, especially knee flexion and stretch exercises. When getting out of bed and walking, pay attention to safety and prevent falls.
- The pain will gradually decrease. If necessary, take painkillers prescribed by the doctor or apply ice packs.
- Please control your weight and adopt a balanced diet. Please avoid kneeling, running, jumping, climbing or lifting heavy objects within 3 months after the operation.
- If tooth extraction or other operations are performed, the doctor must be informed first that there is an artificial knee joint, and preventive antibiotics should be taken. Please keep the skin of the lower limbs intact. If the broken skin or tinea pedis are found, which need to be treated in time.
- After artificial knee replacement, bruises on the thighs and calves and slight swelling of the joints will occur for about three months, and the warm feeling will last for about six months. Please do not worry too much. If there are abnormal signs such as fever, discharge from the wound, increased pain, etc., please return to the "Orthopedic Clinic" immediately.
References
- Davila Castrodad, I. M., Recai, T. M., Abraham, M. M., Etcheson, J. I., Mohamed, N. S., Edalatpour, A., & Delanois, R. E. (2019). Rehabilitation protocols following total knee arthroplasty: a review of study designs and outcome measures. Annals of Translational Medicine, 7(Suppl 7), S255. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.08.15
- Li, T. N., & Zhuang, Z. H., (2022). Total artificial knee replacement and home care. Changhua Nursing, 29(1), 12-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.6647%2fCN.202203_29(1).0003
- Wang, K. Y., Chen, S., & Lin, L. H. (2018). Musculoskeletal disorder and nursing. In K. Y. Wang (Ed.), Medical surgical nursing (5th ed., pp. 55-62). Taipei City, Taiwan, ROC: Yeongda.
Quiz
Please answer the following questions:
Nursing Instruction Satisfaction
Please log in to rate
- Location
-
- Category
- Surgery / Procedure